Staying active and healthy: nutrition and physical activity important with GLP-1 RA medications

Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been used in treating diabetes for nearly 2 decades. Effective in chronic weight management and helping reduce the risk of serious heart problems in adults with obesity or overweight, such therapies are becoming a valuable tool for addressing the chronic disease of obesity. Good nutrition and regular physical activity are essential to maximize the benefits of these medications and support active aging.

What are GLP-1 RA medications?
GLP-1 RA medications (see Table) work by mimicking natural hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 that are stimulated by eating and help to regulate appetite and blood sugar levels. The medications can significantly reduce appetite and food cravings, slow digestion and increase feelings of satiety, which can lead to lower food consumption and substantial weight loss. Common side effects can include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation which can make maintaining good nutrition more difficult.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) medications
| Brand Name (Generic Name) | Approved Use by Food and Drug Administration* |
|---|---|
| Wegovy® (Semaglutide) | Reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in adults with obesity or adults with overweight and at least one weight-related comorbidity, reduce risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with CVD and obesity or overweight |
| Ozempic® (Semaglutide) | Improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes, reduce risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and CVD |
| Rybelsus® (Semaglutide) | Improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes |
| Mounjaro® (Tirzepatide) | Improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes |
| Zepbound® (Tirzepatide) | Chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related comorbidity |
| Saxenda® (Liraglutide) | Chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related comorbidity |
| Victoza® (Liraglutide) | Improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes, reduce risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and CVD |
| Trulicity® (Dulaglutide) | Improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes, reduce risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and CVD or multiple cardiovascular risk factors |
| Byetta® (Exenatide) | Improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes |
Risk of muscle loss and why it matters
Weight loss can lead to significant changes in body composition, including muscle loss. A 2021 clinical trial of a GLP-1 RA medication showed approximately 40% of the weight lost was lean body mass, including muscle. This can be especially challenging for older adults because muscle naturally decreases with age. Studies have documented muscle mass decreases about 3% to 5% per decade after middle-age and decreases at a faster rate after the age of 75.
Some older adults may not be too concerned about muscle loss when they are rapidly losing weight. Others may believe that a focus on building and maintaining muscle means “bulking up.” Yet, muscle is needed for good health including everything from supporting movement and bone and joint function to reducing fall risk and maintaining insulin sensitivity.
Protein can help make a difference
Nutrition interventions, particularly higher protein intake can help reduce muscle loss during weight loss. In general, older adults should aim for a protein intake of 1.0 to 1.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. For a 150-pound (68 kilogram) older adult, this translates to about 68 to 82 grams of protein every day--roughly 25-30 grams of protein per meal. Good protein sources are lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Oral nutrition supplements can also be a good source of protein and other important nutrients and can be used as part of a meal or for a snack.
Sometimes changes in appetite--whether because of medications or aging--can make it difficult to eat the recommended amount of protein. A registered dietitian nutritionist can help provide more specific nutrition guidance.
Tips for Getting More Protein
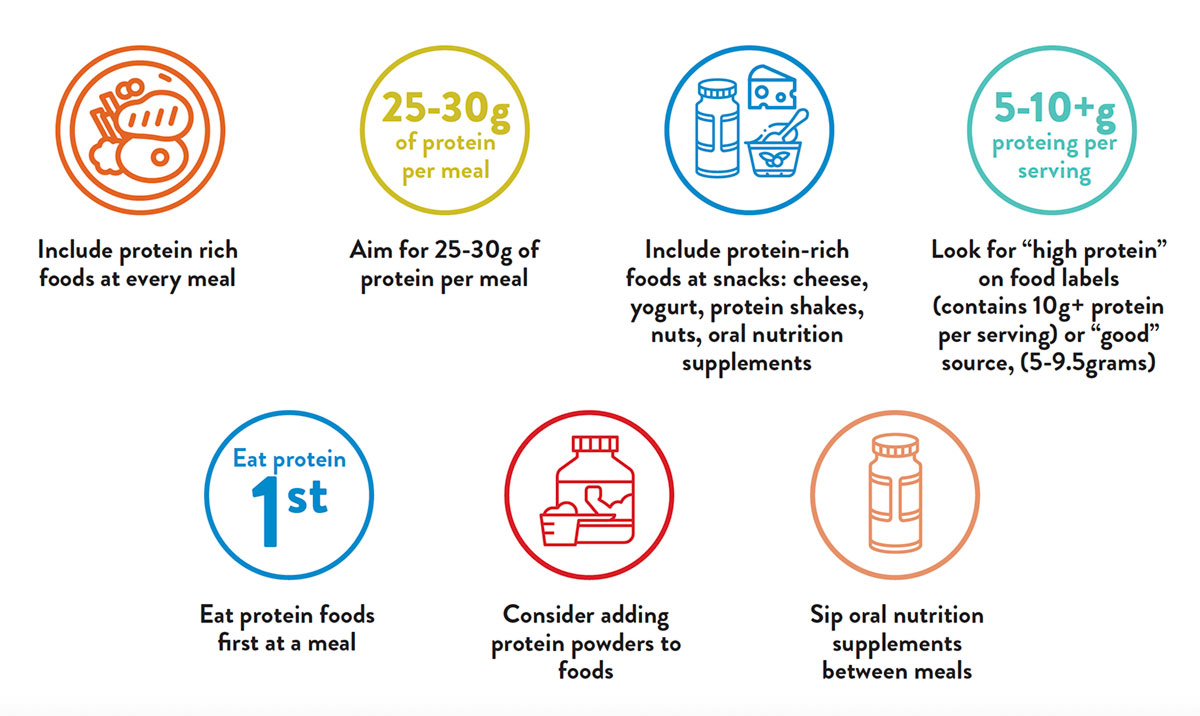
Along with protein, meals that have a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help older adults reach recommendations for essential vitamins (particularly B vitamins), minerals, and fiber. Adequate hydration is also important for active older adults on anti-obesity medications, as GLP-1 RA therapies may lead to reduced thirst.
Physical activity also critical for muscle health
There are many benefits of regular physical activity for older adults, including helping maintain muscle health. For individuals using GLP-1 RA medications, physical activity may help optimize preserving muscle. In addition, it is important to continue regular physical activity when GLP-1 RA medications are discontinued, which may help maintain weight loss and muscle. General physical activity recommendations for older adults are at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week and two days of activities that strengthen muscles (such as resistance training and isometric exercises), along with activities to improve balance (could include yoga or Tai Chi). Older adults should engage in physical activities that they enjoy and are suitable for their fitness levels and any medical conditions they may have. Walking, swimming, and dancing are excellent options.
GLP-1 RA medications can be an effective tool for managing obesity and should be supported by a balanced diet rich in protein and regular physical activity to support muscle and healthy aging.
Share